This is the first post of many that are to come from things I’ve learned in Human Anatomy class. I am typing up this info to help me memorize and use my blog for my own personal development and success in school.
Different types of anatomy
- Gross anatomyinvolves anything that could be seen with your unaided eye.
- Surface anatomy is a subset of gross anatomy that is anything that can be revealed on the skin.
- Microscopic anatomy is known as histologywhich is the study of tissues. This is the very basis of anatomy.
- Histo=web or tissue and -logy=Study of.
- Developmental anatomyis the development of anatomy.
- Embryological anatomy is a subset of developmental as it’s limited to the embryo inside the womb.
- Pathology anatomy has to do with specimens like biopsies and such.
- Radiographic anatomy has to do with X-Ray’s, CT-Scans, etc
Anatomical Terms of Location
Anatomy terms are based on ancient Greek or Latin so that medical terminology is standard nomenclature worldwide.
The anatomical position is a person standing erect, with their feet together, eyes forward, palms facing anterior (front) with the thumbs pointing away from the body. All the terms below apply to the body when it’s in the anatomical position.
- Superior (cranial) means toward the head.
- Inferior (caudal) means toward the feet. Cauda is latin for tail because the bottom of the spine resembles a tail. A horse’s tail is known as a cauda equina for example.
- Anterior (ventral) means front.
- Posterior (dorsal) means back. These are both veterinary terms that are also used for humans. (i.e. dorsal-fin of a dolphin.)
- Medial means toward the middle.
- Lateral means to the sides.
- Proximal means in or near attachment point in equestion, similar to the word proximity.
- Distal means away from the attachment, similar to the word distant.
- Superficial (external) is something on the outside.
- Deep (internal) is inside, away from the skin.
- Ipsilateral: Same side. (Ipsi means same. Lateral means side.)
- Contralateral: Opposite side. (Contra means opposite.) i.e. The right hand is contralateral to the left foot.
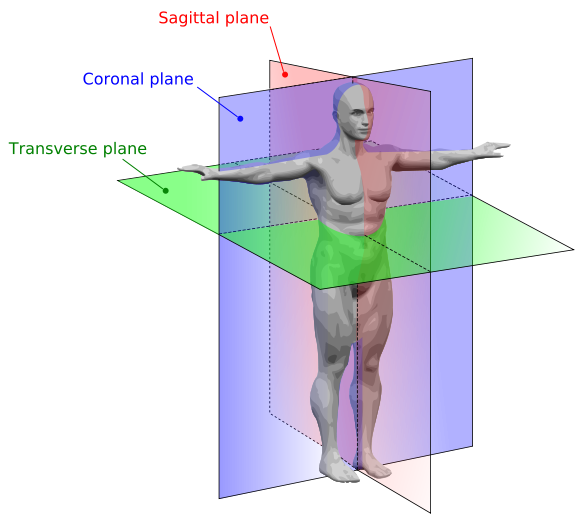
Planes (of existence)
The frontal plane aka coronal is the flat plane that would be created if you were to cut a person vertically, from the left to the right. Shaded blue below.
The sagittal plane is a vertical plane from back to front (dorsal to the ventral, or anteroposteriorly). Mid-sagittal or Median plane refers to the plane being perfectly in the center. Shaded red below
Transverse plane is someone cut horizontally. Shaded in green.
Body cavities
- Dorsal body cavity contains the vertebral and cranial cavity.
- Ventralbody cavity contains the thoracic, diaphragm, abdominal and pelvic cavities.
- The thoracic contains the heart (pericardial) and lungs (the pleural cavity, just remember pleural as plural, because there’s 2 lungs).
Body Cavities with serous membranes: Pleural, pericardial and peritoneal cavities.
Serous cavities are lined by a serous membrane that produces a lubricating fluid (called serous fluid) and its existence creates a very thin, slit-like potential space between layers to allow movement and reduce friction. The inner layer is known as visceral serosa. The outer layer is known as the parietal serosa.
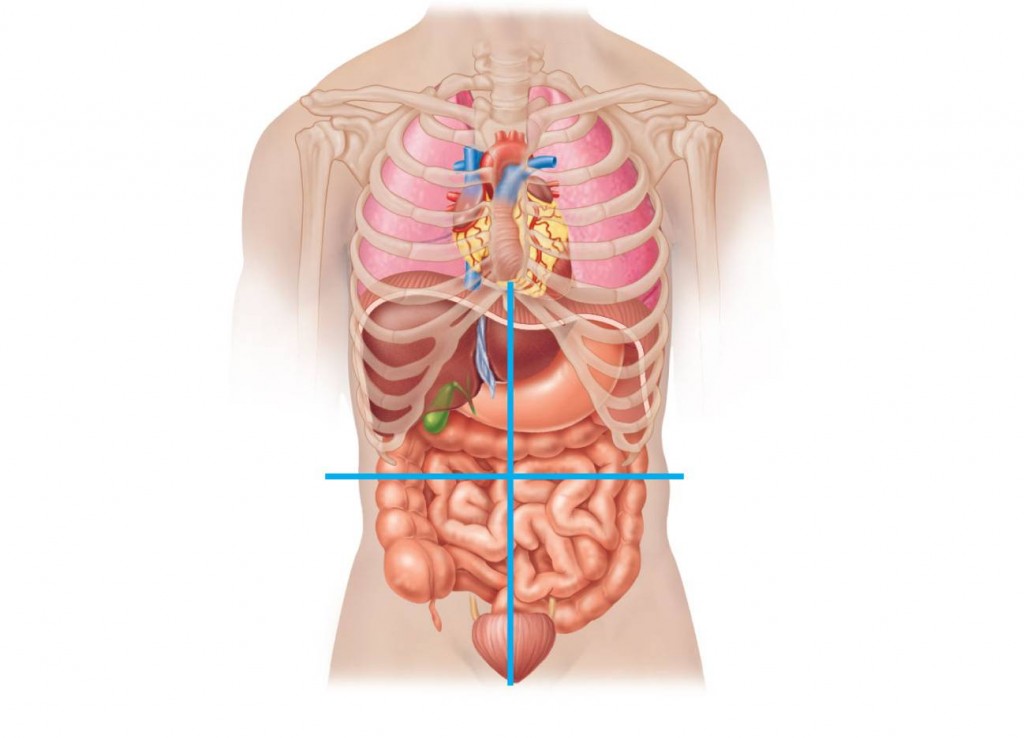
The first way you could identify abdominal regions:

Hypochondriac: Hypo- means below and -chondria means cartilage in ancient greek so hypochondriac means the soft tissue below the heart, between the ribs and navel area.
What does this have to do with the modern use of the word hypochondriac? Hundreds of years ago, the word hypochondria used to be used as a general term when the physician couldn’t pinpoint problems related to pain or issues in the abdominal region of the body, which used to happen often. With time the meaning of the word shifted so that it came to mean, not an illness the physician had no other name for, but an illness that the physician didn’t actually believe was there.
Hypogastric: Gastric means stomach, it means below the stomach, close to the pubic region.
Iliac is synonymous with Inguinal which is the same as groin.
Epigastric: Epi means above, so it means above the stomach.
The second way you could identify abdominal regions:
Microscopic Anatomy
Microscopy means to examine small structures using the microscope. That microscope can be either a light microscope (uses light) or electron microscope (uses beams of electrons). When a specimen is fixed it means you are preserving it. When it is sectioned it means you cut it. Artifacts are minor distortions that happen from the act of cutting something. Under the microscope the tissue doesn’t look exactly the way it would if it was still living and not sectioned off. Light microscopy uses acidic and basic stains while electron microscopy uses heavy metal stains.
Clinical Anatomy: X-rays are best for visualizing bones while Computed (axial) Tomography Scans take multiple x-rays of the body and compile 3D images to get great detail. The PET scan (Positron emission tomography) forms images by detecting radioactive isotopes injected in the body. A sonogram is safe and often used to see unborn babies. An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) produces high quality images of soft tissue and distinguishes body tissues based on relative water content.
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT THE BASICS.






