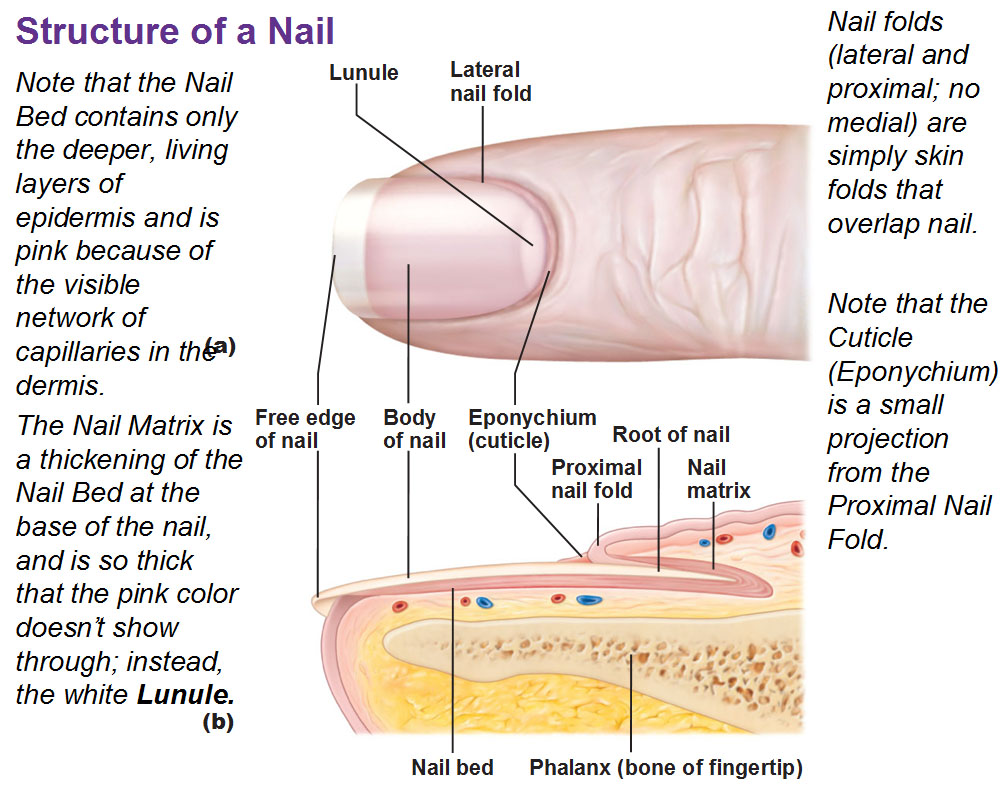
Nails are modified skin: a scale-like modification of epidermis. They have dead keratinized cells which contain hard keratin. The nail bed is epithelial tissue. Underneath it is connective tissue.
Eponychium is the fancy word for cuticle.
Functions of hair
Hair is mainly used for sensation. Hair protects from UV radiation and heat loss. Eyelashes and nose hairs protect from dust.
Structure of hair
Hair is filled with the hard keratin and has two parts: Root (in the skin) and Shaft (above skin)
Three concentric layers of keratinized cells:
Medulla (center) is latin for marrow and refers to the middle of something.
Cortex (immediately surrounds medulla) is several layers thick and,
Cuticle layered like shingles of a roof that helps the hair from sticking together.
The rest of the stuff around the wall is the follicle wall and is super thick.
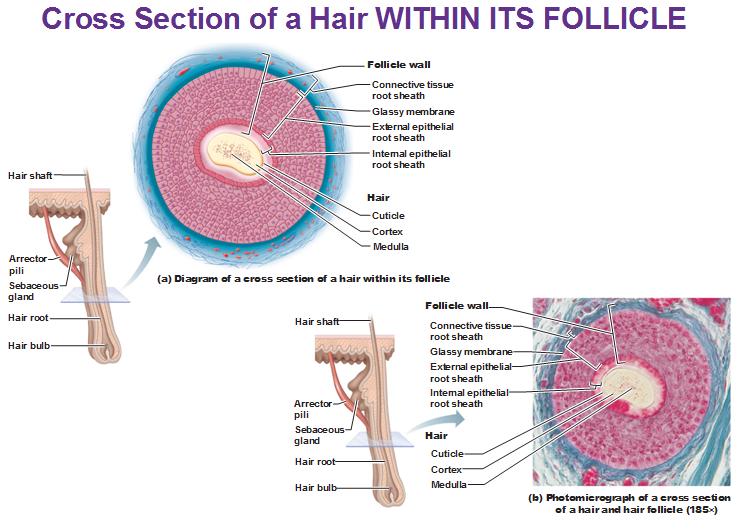
The root is shaped like a bulb. Nerve endings surround each bulb and can sense movement of the hair.
Dermal Papilla enter through the center of the follicle to give oxygen and nutrients because it has capillaries. The hair matrix is where cell reproduction (keratinocytes) occur and melanocytes are generated.
The arrector pili muscle is smooth muscle that connects to every hair follicle. The follicle grows at an angle, that’s why the hair grows to the side and the muscle is at an even greater angle and when it contracts, the muscle allows the hair to stand up.
Types and growth of hair
The shaft of the hair determines its texture. If it’s flat it’ll be curly/kinky, if it’s oval it’ll be wavy and if it’s a circle it’ll be straight.
Vellus hairs = hairs on women and children.
Terminal hairs = manly body hair, pubic, scalp, axillary hair
With age, terminal hairs get replaced by vellus hairs.
Sebaceous Glands = Oil Glands
Sebaceous glands are associated with every hair follicle. Found everywhere over the body except palms and soles; simple branched alveolar gland. Sebum=oil. Glands fill until the cells burst and travels up the duct alongside the follicle wall. This is known as holocrine secretion.
Sudoriferous Glands = Sweat glands
Found everywhere except the nipples and parts of external genitalia.
Sweat is mostly water where, through osmosis, capillaries go through connective tissue and secrete filtrate (fluid inside the blood that is secreted).
Two types of sweat glands, eccrine and apocrine glands.
Eccrine = most numerous, especially on palms, soles and forehead. This is known as true sweat.
Apocrine gland = confined to axillary (armpit), anal and genital areas. This includes fat and proteins that bacteria break down on the skin to create a musky odor called human pheromones that signal info about the genetic makeup of a persons immune system.
A modified apocrine gland is a ceruminous gland that produces ear wax in the external ear canal.
A modified apocrine gland is the mammary gland that secretes milk.
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE






