The building blocks of cells
The cells are the smallest living things in our body. Organelles are little organs within the cells. Cytoplasm is the watery-liquid within the cell and the nucleus is like the brain of the cell. Plasma membrane is like the skin of the cell.
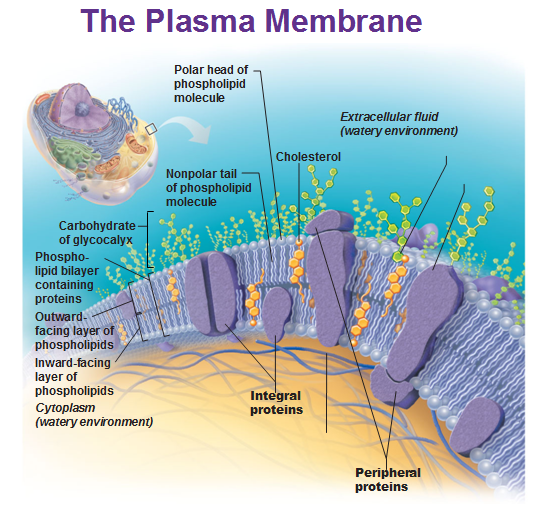
The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. The heads of the structure are made of phosphate that are charged and hydrophilic (likes water) while the tail is made up of lipids (fats) that are hydrophobic (repel water).
We have water inside and outside the cell; water is everywhere. The bi-layer creates the separation between the inside and outside, with the tails pointing at each other and the phosphate facing the inside and outside of cells.
There are proteins such as transmembrane proteins that span the layer to allow things in and out through facilitated diffusion. The integral proteins are firmly embedded in the bilayer while peripheral proteins attach to the membrane surface. Things normally move through diffusion (facilitated diffusion) and osmosis is diffusion specifically for water. Larger molecules may require energy (ATP) to get moved across and do it with the help of proteins that change shape to allow these molecules through (active transport).

There are three types of endocytosis: Endo means inside and cyte means cell, so this is the process of something entering a cell.
- Phagocytosis = cell eating (phago is greek for “to devour”)
- Pinocytosis = cell drinking (pein is greek for “to drink”)
- Receptor mediated phagocytosis is more specific b/c it can only take in specific molecules that match the proteins in the plasma membrane.
Exocytosis is the process of moving substances OUT of the cell. To do that a vesicle is formed that contains waste and is made up of the same material as the plasma membrane and becomes part of the membrane when it’s done.
Cytoplasm consists of cytosol, organelles and inclusions.
Inclusions include pigments, protein crystals, and packets of food called lipid droplets.
Cytosol is the name for the jelly-like substance that makes up cytoplasm and is mostly water.
Ribosomes
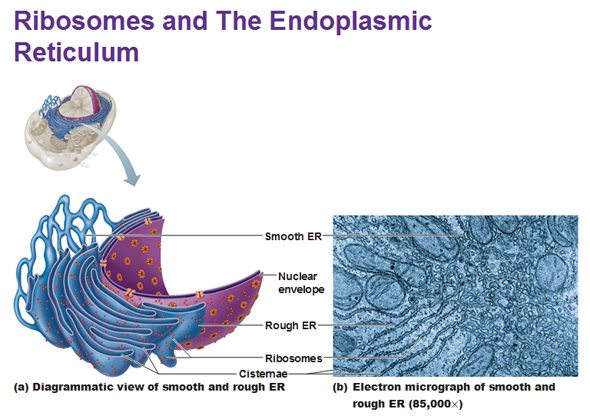
When you look at ribosomes under the light microscope, they are these dark tiny spots. They are made of ribosomal proteins and nucleic acids and they make proteins. Ribosomes are found littered all over the endoplasmic reticulum (reticulum means network) which is what envelopes the nucleus and extends away from it as an assembly line that makes proteins. The fluid filled sacs within the reticulum network are known as the cisternae. Smooth ER doesn’t have ribosomes but rough ER does. Smooth ER breaks up and makes lipids and stores calcium. Muscle cells are full of smooth ER because calcium is heavily needed for contraction.
The Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi Apparatus sorts and packs protein to ship it out. It’s like the Fed Ex/UPS of your cell. It looks just like E.R. and is also made up of the phospholipid bilayer just like ER and plasma membrane. Pieces of it pinch off to create vesicles that carry the protein toward the plasma membrane. When it releases its content, it simply blends with the plasma membrane and becomes a part of it. If it doesn’t want to release the vesicle to the outside but instead wants to kill a bacteria within the cell, it can connect and merge with the vesicle that contains the bacteria and kill it.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are vesicles filled with digestive enzymes that devour unwanted substances such as bacteria and digest them. Enclosing digestive enzymes within a cell membrane protects the rest of the cell form being digested. Peroxisomes carry oxidase enzymes that neutralize free radicals, poisons, and break up fats. Peroxisomes are found heavily in the liver and kidneys and are the toxic waste removal system of the cells. 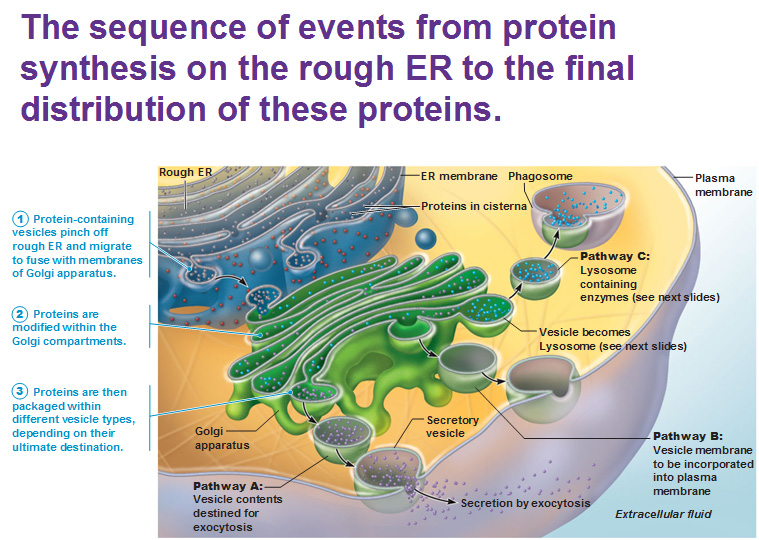
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are like the power plant of the cell. They generate most of the energy within a cell. These are the most complex organelles in a cell and are what break down glucose to make ATP, which is a tiny molecule that can be used to power chemical reactions such as pumping ions across a membrane.
Cytoskeleton
The cell skeleton is made up of 3 types of protein rods that give cells their structure. From smallest to largest:
Microfilaments are made of spherical proteins/subunits called actin. (Example: Microvilli)
Intermediate filaments are made of tough, fibrous, long proteins called keratin that are twisted together like a rope to create structure. (Example: Desmosomes)
Microtubules are made of spherical proteins called tubulin subunits which come together to create a thick, hollow rope. (Example: Cilia)
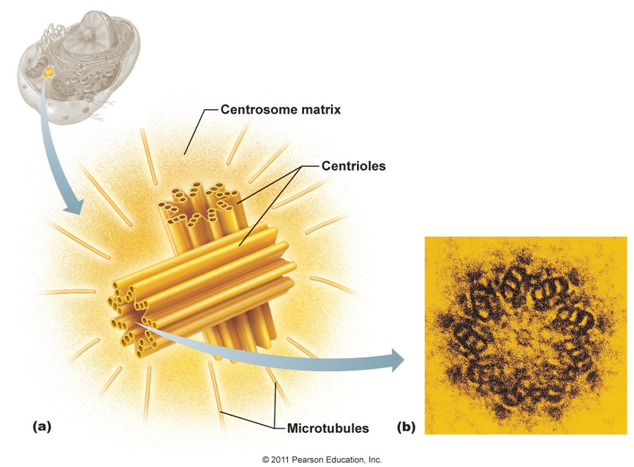
Centrioles are 9 sets of 3 microtubules that are arranged in a circle to create a centrosome. A centrosome is a pair of centrioles. A centrosome can move or change shape to become cilia or flagella or create the spindle during mitosis (cell division). The seemingly random microtubules surrounding a centrosome are what bind centrosomes to pull a cell apart during cell division.
The nucleus and DNA — the control center of cell
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT THE BASICS.






