Cerebral white matter tends to be mostly myelinated axons bundled into large tracts that allow the different areas of the cerebral cortex to communicate with each other as well as with the brain stem and spinal cord.
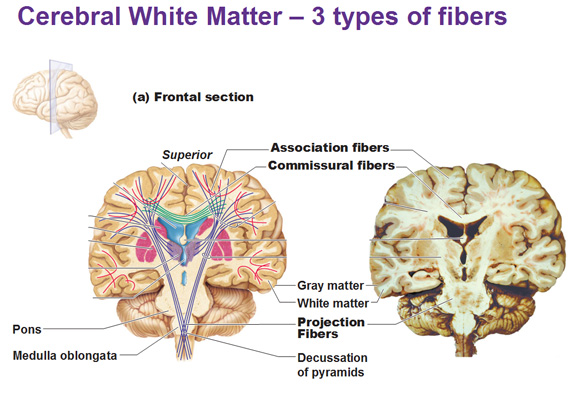
Association fibers are the ones in red connecting different parts of same hemisphere.
Commissural fibers are in green. They run horizontal and are what create the corpus callosum. They connect corresponding gray areas of right and left hemispheres.
Projection fibers in blue run vertically, ascending and descending to and from spinal cord. Where they connect is the decussation of pyramids. Decussation in biology means an intersection intersection or crossing of two tracts that form the letter X.
Cerebral gray matter
Groups of brain nuclei deep within the cerebral white matter
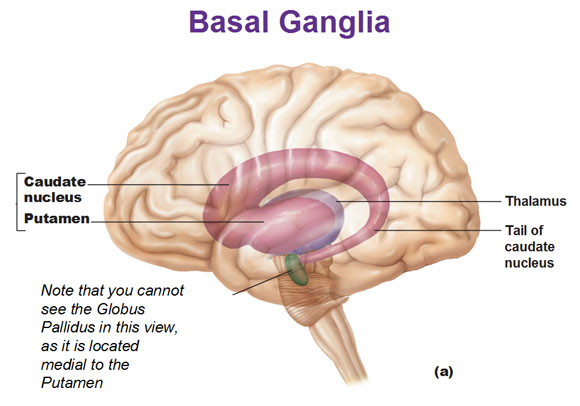
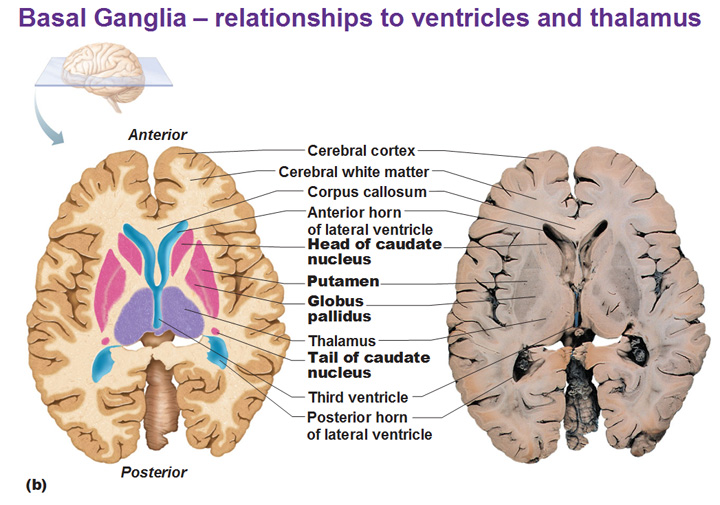
Basal ganglia – This is the least well known of all the structures because of how deep it is. It helps us understand habits and to feel the passage of time. It also controls motor movements, specifically regulating the intensity of movements.
Basal forebrain nuclei – memory
Claustrum – subconscious visual processing
Amygdala – part of Limbic System where we store our fears (associates w/ memories in hippocampus)
Note that we will only be discussing the Basal Ganglia group in detail for this blog post. Also note that as research continues, the name “Basal Ganglia” is falling out of favor.
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT THE CNS