Basics of Epithelial Tissue
Tissue is any group of cells of similar structure that perform a common function. They also have a nonliving material between the cells called the extracellular matrix which we will discuss in detail later.
There are 4 basic tissue types:
- Epithelial (covering)
- Connective (support)
- Muscle (movement)
- Nervous (control) tissue
Epithelial tissue covers a body surface or lines a body cavity and is present on almost all glands.
Functions of Epithelia
- Protection of underlying tissues
- Sensory reception via nerve endings/receptors
- Diffusion (movement of molecules down their concentration gradients)
- Absorption (taking molecules into cells)
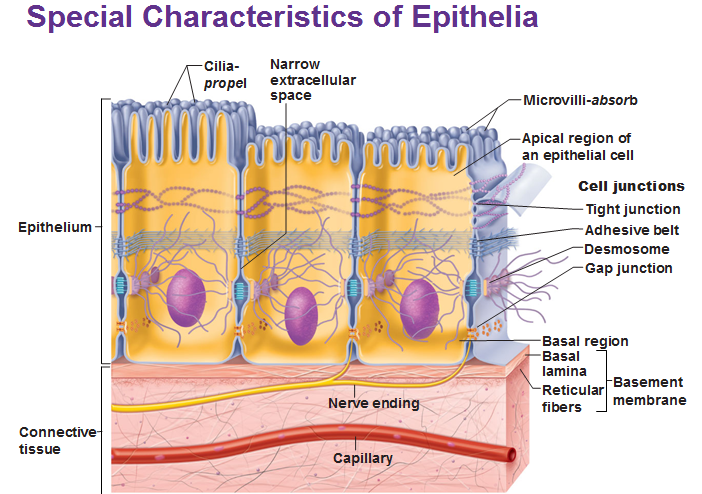
- Note role of Microvilli in pic above (to absorb)
- Secretion (releasing molecules from cells)
- Ion transport (moving charged ions across the tissue)
- Filtration (removal of molecules from fluid)
- Forms slippery surfaces (production of mucus)
- Note role of Cilia in pic above (to propel)
Special characteristics of Epithelia
- High Cellularity (cells separated by minimal amounts of ECM)
- Specialized contacts (cells joined by special junctions)
- Polarity (Apical surface differs from basal surface)
- Supported by layer of connective tissue (includes a basement membrane)
- Avascular (has no blood vessels) but innervated (has nerves). It receives nutrients from underlying connective tissue where capillaries lie.
- Regeneration (lost cells are quickly replaced by mitosis)
How to Classify Epithelia
First name of tissue indicates number of cell layers
- Simple—one layer of cells
- Stratified—more than one layer of cells
Last name of tissue describes shape of cells
- Squamous—cells are wider than tall (plate-like) – “squashed”
- Cuboidal—cells are as wide as tall, like cubes
- Columnar—cells are taller than they are wide, like columns

Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT EPITHELIAL AND CT






