The Immune System
The immune system is a specific part of the system that’s going to recognize anything that’s foreign and try to get rid of it. The immune system becomes more efficient with the destruction with each subsequent exposure.
Lymphocytes
Our super most important cells are our lymphocytes which are a type of white blood cell.
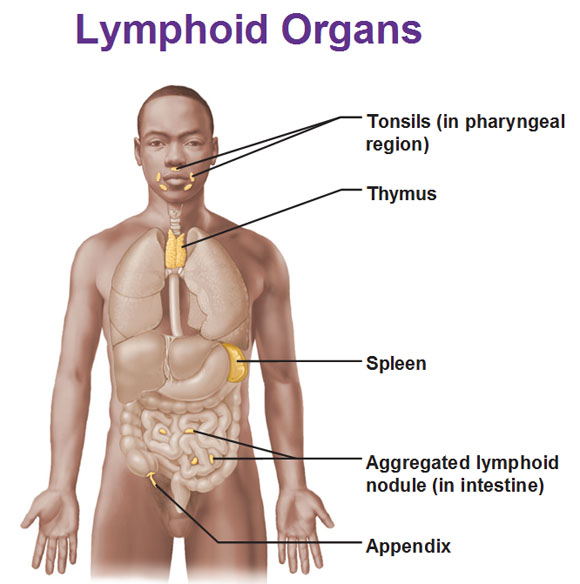
The lymphoid organs that contain lymphocytes are the lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, aggregated lymphoid nodules in small intestine, and the appendix.
Three classes of lymphocytes: T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes and NK (Natural Killer) cells. These all originate and are made from the red bone marrow. T matures in the Thymus. B matures in the Bone marrow. The Natural Killer cells grow up in the bone marrow and are capable of killing a wide variety of infected cells and some cancer cells.
T-Lymphocytes
T-lymphocytes make up 70-85% of the lymphocytes in our bodies. There are two main groups: Helper T cells and Cytotoxic cells and have been given numerical names, T4 and T8.
There are different types of Helper T-lymphocytes and each one responds to a specific type of antigen (anything that is a foreign shape or projecting from a surface). They are the ones that initially do the recognition. These are the cells that HIV really likes to inhabit and use, like pirates. All viruses are like pirates that like to enter into cells and each virus has a cell of choice. Just like how pirates get on a ship and use the ship they get, along with the cannons, to hijack other ships. A virus wants to replicate itself but it doesn’t have enough machinery on its own to do it. Viruses use DNA and mRNA for making their own proteins. So the virus is going to repackage all these cells until the cells explode. So they blow up the ship, and go get 1,000 more ships and then repeat the process. HIV specifically enters into these helper T-cells, reproduce and blow up the ship. This exponentially increases and the problem is that these are knocking out the immune system at the core. Usually it’s another infection that eventually wipes out the patient and not the actual HIV that does it because their defenses are down.
We aso have cytotoxic T-lymphocytes which respond to one type of foreign thing (antigen) but these are the ones that actually do the killing. After a helper cell does the recognition, they attach to the target cell and secrete substances that will cause the target cell to burst.
B-lymphocytes
These make up about 15-30% of the lymphocytes. Each one responds to one specific antigen but only after they are activated by a T-cell that’s recognized something. The T-cell presents the information to the B-cell and it responds by making antibodies. Another name for antibodies are immunoglobulins. They have a very specific shape that helps mark foreign antibodies so that they could be marked for destruction. Some of these B-cells, instead of producing and releasing antibodies, will quietly be activated by the T-cells and linger in the background as memory-B-lymphocytes to mount a quicker immune response the next time the same antigen shows up.
Lymphoid Tissue (MALT and Lymphoid Organs)
Lymphoid tissue is specialized connective tissue where huge numbers of lymphocytes gather to fight pathogens. Two general locations are the lymphoid organs and the Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT).
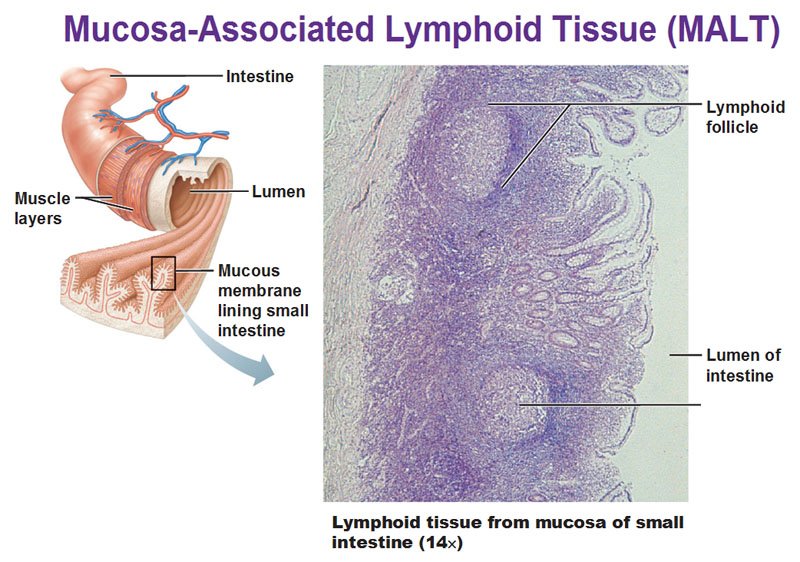
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT) includes the mucous membranes of digestive, urinary, respiratory, and reproductive tracts. This particular tissue below is found in the small intestine in these little patches/globs buried inside the mucosa of the small intestine.
 Lymphoid Organs: Bone marrow (not shown) produces B-Lymphocytes and the Thymus produces T-lymphocytes. These other organs store lymphocytes and gather/destroy pathogens. The Spleen curves around the left side of stomach and is the largest lymphoid organ. It removes antigens and old/defective blood cells from the blood and stores platelets.
Lymphoid Organs: Bone marrow (not shown) produces B-Lymphocytes and the Thymus produces T-lymphocytes. These other organs store lymphocytes and gather/destroy pathogens. The Spleen curves around the left side of stomach and is the largest lymphoid organ. It removes antigens and old/defective blood cells from the blood and stores platelets.

Spleen
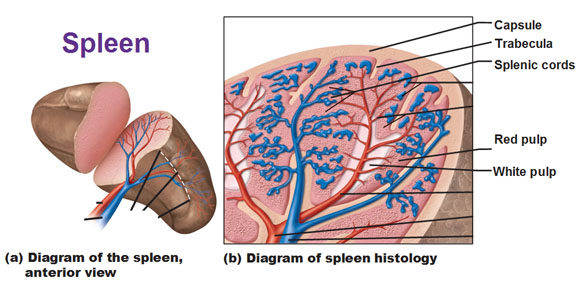
The spleen is that organ that can be confused with a kidney hanging out by the pancreas. That spleen is made up of lymphoid tissue that resembles a giant lymph node when you cut it in half. We have red pulp and white pulp, with lymph circulating through, being cleansed but also specifically the red pulp takes care of dead red blood cells.
The red pulp surrounds the white pulp. It is composed of venous sinuses, splenic cords and it’s where macrophages phagocytize worn out RBC’s. (red pulp for red blood cells)
The white pulp is what provides the immune function of the spleen and is made of thick sleeves of lymphoid tissue. Here is where blood-borne antigens are destroyed as they are activated by the immune response. (white pulp for white blood cells).
In the picture below, the trabeculae are what divide the spleen into sections, just like the trabeculae found in lymph nodes.
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT THE SPECIALIZED SYSTEMS






