Intro to the Heart

The heart pumps blood, all around but you can really subdivide the whole heart into two halves and think of it as a double pump. One part pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs to deposit carbon dioxide, pick up oxygen and go to the other side where it’s going to pump the freshly oxygenated blood to the rest of the body until it arrives back to the first part to deposit the carbon dioxide. This double-circuit circulation is the way the heart works in all mammals and prevents deoxygenated and oxygenated blood from mixing.
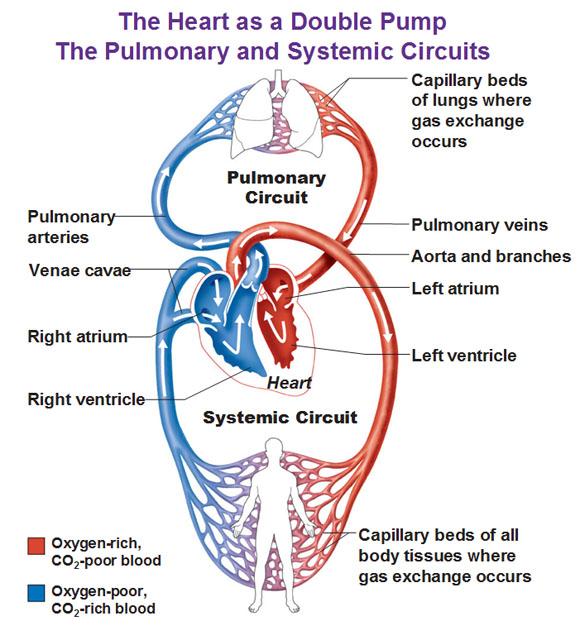
For the picture above: The left blue side is the right side, the left is the right. These blue vessels go to the lungs, and go to enter the left side heart, where the oxygen rich blood (the standard is to display that in red) is going to go to the rest of the body. Gases are exchanged and then the oxygen-poor-blood comes back to the right side. So that’s your overall plan.
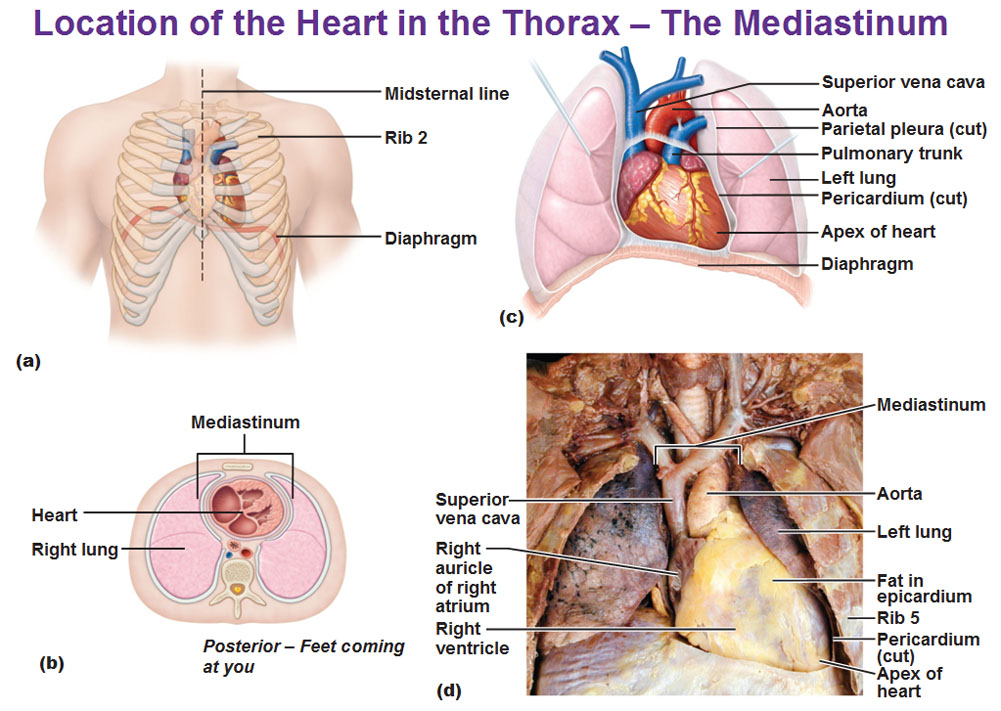 For the picture above, starting with the top left view, we could see the heart is located inside the chest. You see the ribs surround it and the heart is behind the sternum there. There’s more of it located on the left side than right side. The heart is contained in the portion of the chest known as the mediastinum. The mediastinum is the “middle” section of the chest cavity. The picture on the top right shows it in place with the lungs that lie on either side of the heart. You could see there’s a cut out in the lungs to allow the heart to fit. The bottom left picture is the location of the heart if the thorax were sliced so you could get a better idea of its location. It is here that you could see mediastinum does not include the lungs. The bottom right is a view from a cadaver.
For the picture above, starting with the top left view, we could see the heart is located inside the chest. You see the ribs surround it and the heart is behind the sternum there. There’s more of it located on the left side than right side. The heart is contained in the portion of the chest known as the mediastinum. The mediastinum is the “middle” section of the chest cavity. The picture on the top right shows it in place with the lungs that lie on either side of the heart. You could see there’s a cut out in the lungs to allow the heart to fit. The bottom left picture is the location of the heart if the thorax were sliced so you could get a better idea of its location. It is here that you could see mediastinum does not include the lungs. The bottom right is a view from a cadaver.
Representative colors of Arteries and Veins
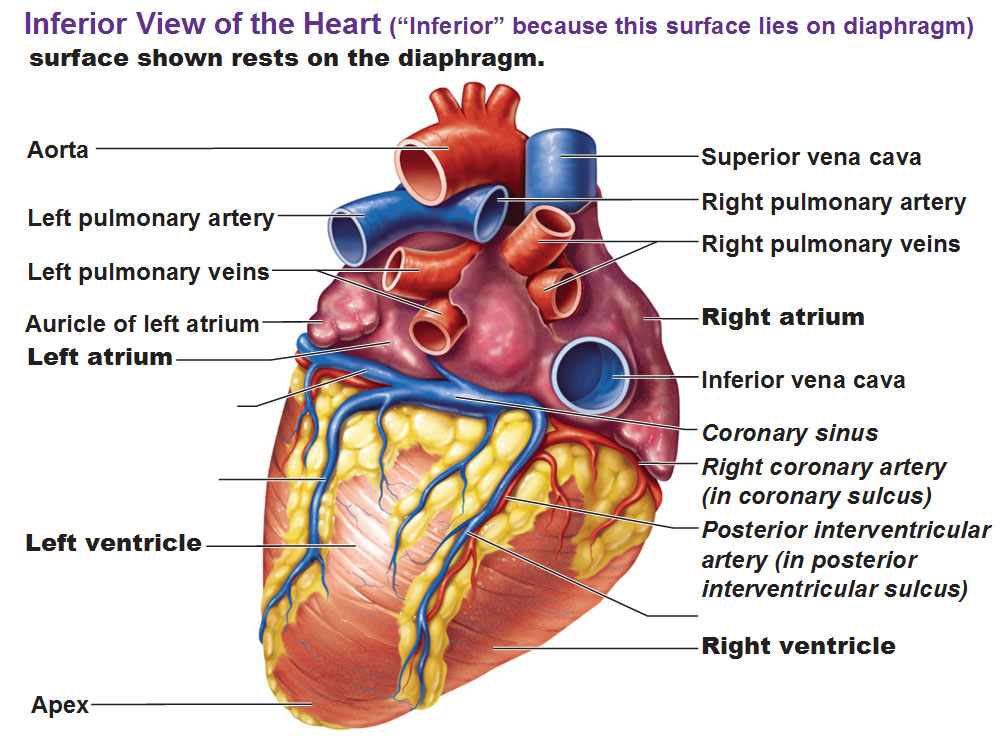
Note that arteries, which carry blood away from the heart, are indicated in red (for oxygen-rich blood) and that veins, which carry blood toward the heart, are indicated in blue (for oxygen-poor blood).
However, there is an exception here. Note the color of the pulmonary trunk, which is an artery carrying oxygen-poor blood, and of the pulmonary veins, which are veins carrying oxygen-rich blood. So in other words, just because a blood vessel is going away from the heart because it’s an artery, doesn’t mean it’s full of oxygen. The pulmonary trunk carries oxygen poor blood away from the heart and straight into the lungs to be replenished with oxygen, that’s why it’s blue. The pulmonary vein carrying blood toward the heart is red because it is coming immediately after being filled with oxygen from the lungs.
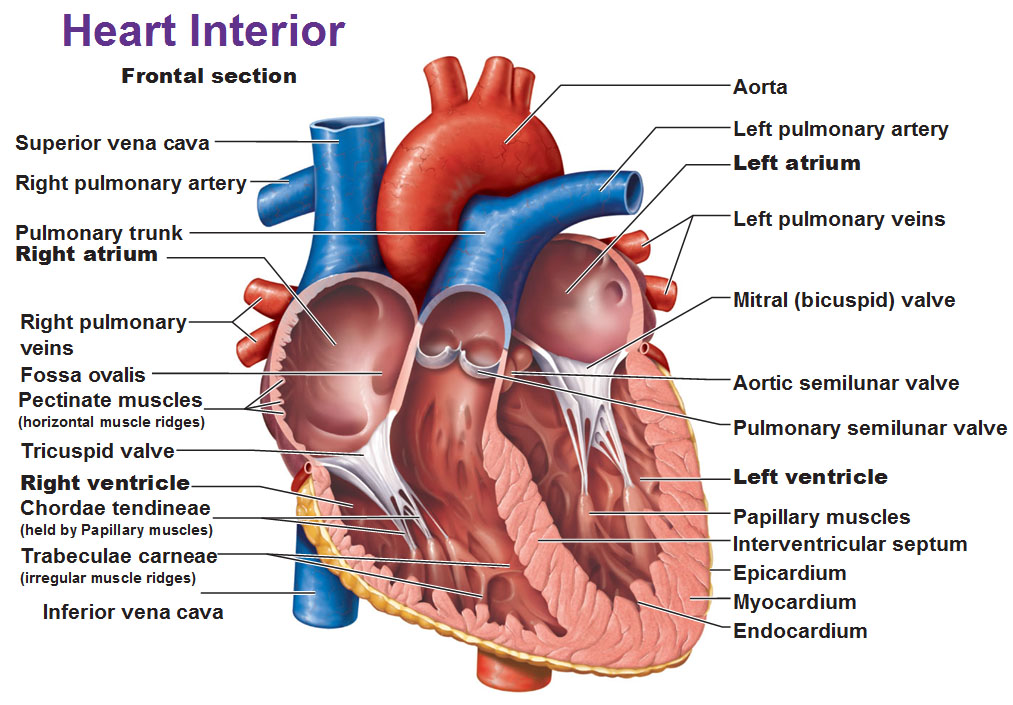
Cool mnemonic to not confuse the bicuspid/tricuspid valves. Just relate them to the lobes of the lungs.
The left atrioventricular valve is the BIcuspid valve (aka mitral valve). Just like how the left lung has TWO lobes (bi).
The right atrioventricular valve is the TRIcuspid valve. Just like how the right lung has THREE lobes (tri).
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM