Detailed Features of Epithelia
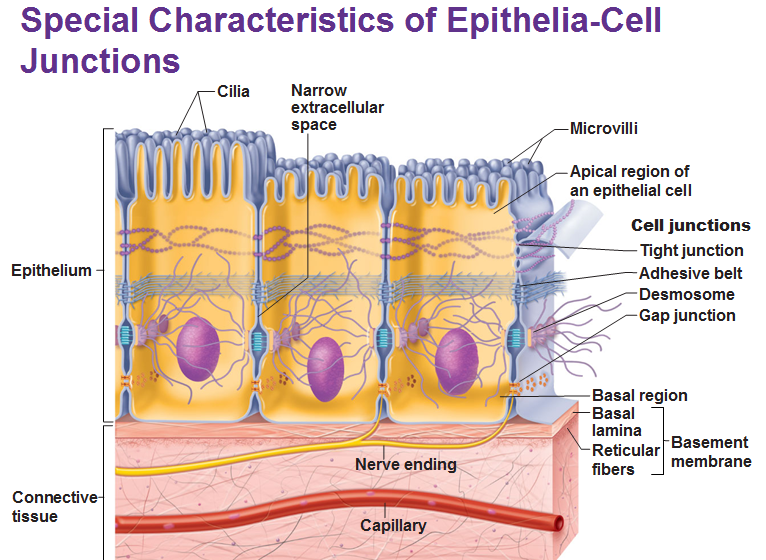
Cell junctions
Tight junctions are impermeable junctions that prevent molecules from passing through intercellular space. They are found at the apical (think of apical as, a-peak.. as in, the top) region of most epithelial tissue types. Some proteins in the plasma membrane of adjacent cells are fused/interlocked. They prevent certain molecules from passing between cells of epithelial tissue.
An adhesive belt anchors adjacent cells. A transmembrane linker protein attaches to actin microfilaments of the cytoskeleton and binds adjacent cells.
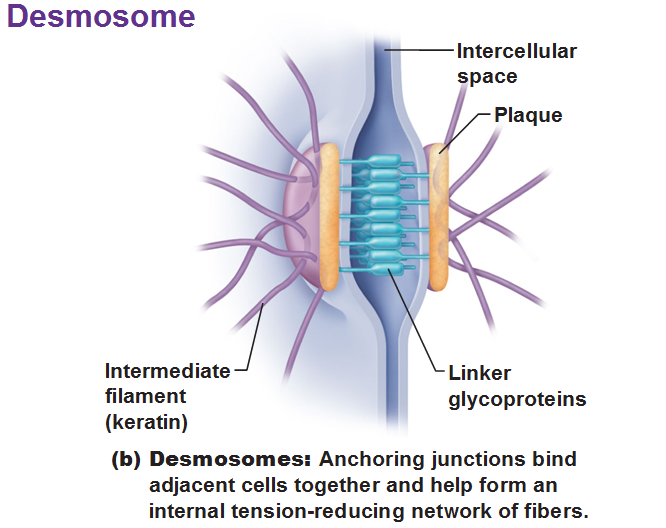
Desmosomes are the main junctions for binding cells together. They are scattered along abutting sides. The cytoplasmic side of each plasma membrane has a plaque which are joined between cells by the linker proteins. Intermediate filaments go across the cytoplasm and anchor these desmosomes together at opposite sides of cells. Desmosomes are common in cardiac muscle and epithelial tissue.
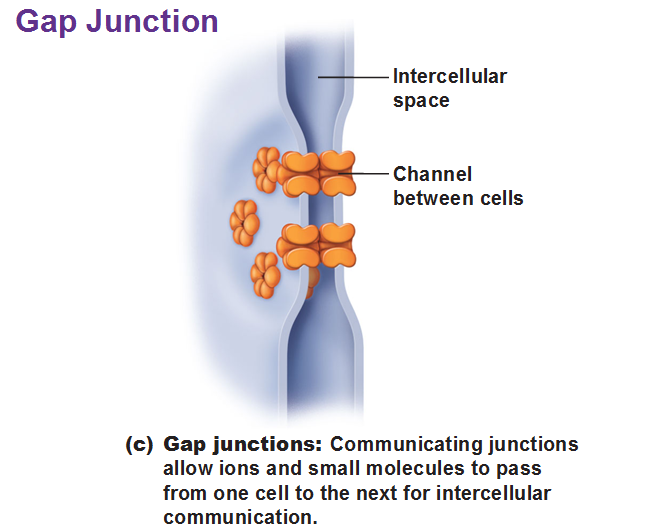
Gap Junctions are passageways between two adjacent cells. They let small molecules move directly between neighboring cells. The cells are connected by hollow cylinders of protein and function in inter-cellular communication.
The Basal Lamina
This provides a scaffolding type of physical support to help regenerating epithelial tissue migrate. It consists mostly of protein and water. It acts as a selective filter determining which molecules from capillaries enter the epithelium.
Basal lamina and reticular layers of the underlying connective tissue deep to it form the basement membrane.
Epithelial Apical Surface Features
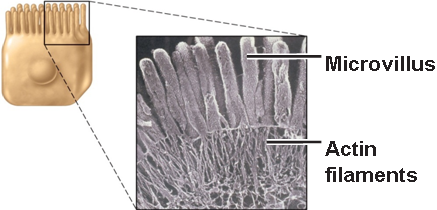
Microvilli are fingerlike extensions of plasma membrane. They are abundant in epithelial tissue of the small intestine and kidneys. They maximize surface area, acting like a filter, and resist abrasion thanks to actin microfilaments at their bases. This concept of surface area occurs frequently in nature.

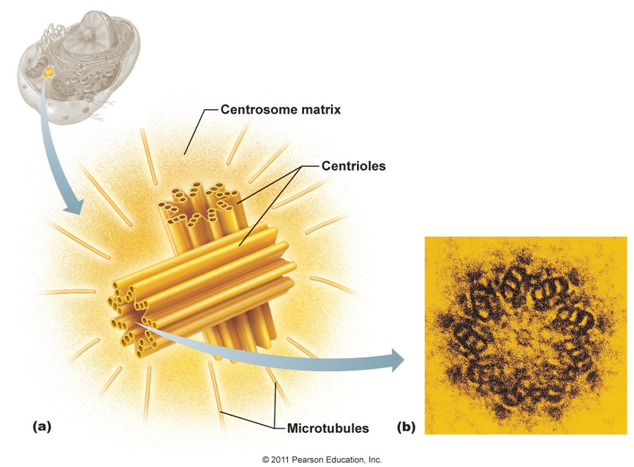
Cilia seem similar but they are not. They are whiplike extensions made of bands of microtubules and move in waves. Each cilium contains a core of nine pairs (“doublets”) of microtubules encircling one central pair, similar to a centriole, which has nine triplets in a circle. (Centrioles are 9 sets of 3 microtubules that are arranged in a circle to create a centrosome. A centrosome is a pair of centrioles.) In fact, an unpaired centriole called a basal body migrates to the site of a future cilium and from that the cilium is generated. The cilium is just this basal body surrounded with plasma membrane as a covering.
Cilium move in one direction thanks to motor proteins called dynein arms and these arms oscillate creating a power stroke followed by a non-propulsive recovery stroke. These proteins hang onto ATP and gather energy in its chemical bonds to make the movement to get rid of mucus.
Flagella are single, extra long cilium to the point of being considered a tail and are only found in sperm cells as they propel the sperm along the female reproductive tract.
Use this Table of Contents to go to the next article

YOU ARE HERE AT EPITHELIAL AND CT






