Organic Compound #2: Lipids
The second class of organic molecules are lipids or fats. The most important characteristic of them is that they are insoluble in water. Think of butter or vegetable oil. The oil or fat will float to the surface of water. When we look at the chemical structure, lipids look like a long chain of carbon atoms with a whole lot of hydrogen atoms attached. When you break these hydrocarbon and carbon-carbon bonds, they release energy measured in calories. Fats contain more calories of energy than any other molecule. Each gram of fat contains nine kilocalories while a gram of carbohydrates contain four kcal’s. The simplest of the fats are called fatty acids which we will start with.
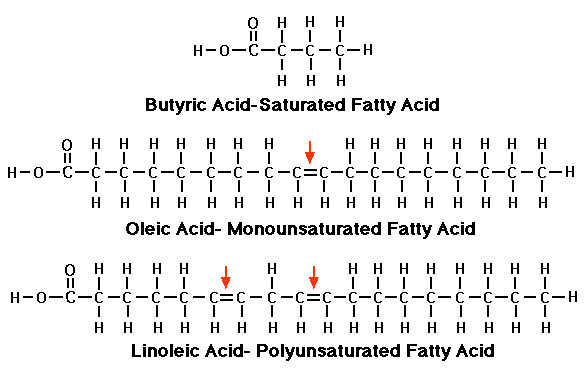
Saturated Fatty Acid
Saturdated FA looks like a long chain of carbons with hydrogen’s. The difference is the terminal carbon has an “carboxylic acid group” attached at the end that is a single bond of OH and double bond of O. This is how it gets the name “fatty acid” because it has this carboxylic acid group. This is called a saturated fatty acid.
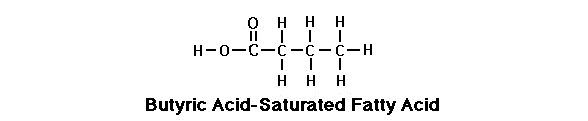
Monounsaturated fat
Monounsaturated fat looks like a saturated FA but you’ll notice between two of the carbons there’s a double covalent bond. Remember we’ve learned that every carbon atom can have only four covalent bonds. Since these two carbons are sharing double bonds, they have fewer hydrogen’s attached to them. So you’ll notice they are missing a couple of hydrogen’s and it’s precisely because of this it is called unsaturated fatty acids: because they are not saturated completely with hydrogen’s. Unsaturated fatty acids have less calories of energy than saturated..
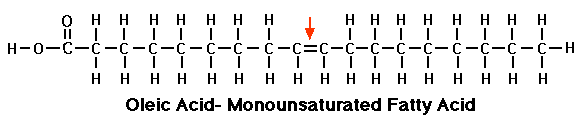
Polyunsaturated fat
This third fatty acid is simply an unsaturated FA, except hydrogen’s are missing in more than one place. That’s why it’s called polyunsaturated fatty acids.
So to recap…
| Saturated FA | Unsaturated FA |
|---|---|
| 1. more C-H bonds (more calories) | Less C-H bonds (less calories) |
| 2. usually solid at room temperature | Usually liquid at room temp |
| 3. Synthesized in animals. (Butter comes from cows and lard comes from pigs and both are solid at room temp.) | Synthesized in plants (corn, safflower, olive oil, sesame seed, peanut oils) |
| 4. Saturated fats and cholesterol increase our risk for atherosclerosis (fat build up on inner walls of arteries). This is the number one cause of death in western countries. Also for that reason, the number one most prescribed drug in the world is Lipitor. | Fats in plants don’t increase our risk of atherosclerosis. |
Chart of the most common fats or oils we use
| Fat or Oil | Saturated | Unsaturated |
|---|---|---|
| Safflower oil | 9% | 91% |
| Sunflower oil | 11% | 89% |
| Corn oil | 13% | 87% |
| Olive oil | 14% | 86% |
| Soybean oil | 15% | 85% |
| Peanut oil | 18% | 82% |
| Cottonseed oil | 27% | 73% |
| Lard | 41% | 59% |
| Beef Tallow | 52% | 48% |
| Butter | 66% | 34% |
| Palm Kernel oil | 86% | 14% |
| Coconut oil | 92% | 8% |
The oil highest in unsaturated fats is safflower oil. Corn oil is made up of 87% unsaturated fats. Butter is 66% saturated fats and also contains cholesterol. If saturated fat causes atherosclerosis, then there’s a benefit in reducing our consumption of animals and the fat from animals.
Palm kernel oil and coconut oil are really high in saturated fats. Palm kernel oil (from palm trees) and coconut oil are often referred to as tropical oils because they come from the tropics. Coconut oil is most commonly used in non-dairy creamers. The advantage of using coconut oil, despite its high saturated fat content, is that it doesn’t have cholesterol (plants don’t have any cholesterol) and there is no lactose.
How is margarine made?
Margarine is a substitute for butter that is made out of vegetable oils. There are a lot of brands of margarine. Let’s take Mazola oil for example. How did they take corn oil and make it taste like butter?
They do a chemical process that attaches hydrogen’s onto the carbon atoms so it ends up looking and tasting like butter. When they take vegetable oil and add hydrogen’s, it’s known as hydrogenated vegetable oil. These are also known as trans-fatty acids. Now you’ve got something that comes from corn, looks like butter, tastes like butter, and basically has every problem butter has because it’s a saturated fat. Some would say this product is even worse than butter.
Do we even need fatty acids?
Yes but the only ones that are essential are unsaturated fats. Which foods contain unsaturated fats? Plants. Vegetables, grains and so on have the fats that we require.
Prostaglandins
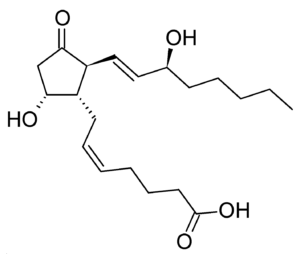
The next group of fats that you may or may not have learned about in a biology class is a prostaglandin. They got that name because they were first identified in the prostates of males but these are actually fats that are associated with every fat tissue cell of the body. Prostaglandins belong to a larger group called eicosanoids.
The importance of a prostaglandin is this: When any cell is injured or suffers trauma, it disrupts the cell membrane. When this phospholipid membrane gets damaged, a chemical process converts some of these phospholipids into prostaglandins. Prostoglandin’s are one of the many chemicals that cause inflammation. Histamines, released from mast cells, cause inflammation as well. In fact, there’s a whole group called chemical mediators of inflammation that contribute to inflammation.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is characterized by four signs: Redness. Warmth. Swelling. Pain. Whenever there’s a disease associated with inflammation, the ending is “-itis.”
So whenever there is injury, that area is going to get red, warm, swollen and hurt like hell. And that’s cause of these chemical mediators of inflammation. So is this good or bad? Inflammation, if it doesn’t go on and on for a long period of time, is good. The inflammatory response is part of the healing process and is known as the non-specific-immune response.
Two examples: (1) Imagine you are hammering a nail and it accidentally hits your thumb. Cells get damaged in this case. Your thumb will get red, warm, swell and hurt. (2) If you have strep throat that means streptococcus bacteria are eating you up. Bacteria are living things that need food. They are looking at your throat and eating parts of your cells. As they start injuring your cells, prostaglandin’s get released and your throat experiences inflammation.
NSAIDs: Non-Steroidal-Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
The typical NSAID is aspirin, ibuprofen (advil, motrin), or naproxen (aleve). These are enzyme inhibitors that reduce inflammation. If somebody has chronic inflammation, such as arthritis, which is inflammation of the joints, and it’s been swollen and in pain for months, then this inflammation is not beneficial and needs to be stopped.
Monoglycerides. Diglycerides. Triglycerides.
The simplified structures of these consists of a three-carbon-molecule known as glycerol. If there is one FA attached to a glycerol, that’s known as a monoglyceride. If there are two FA attached to glycerol, then it’s called a diglyceride. If there’s a third FA attached, it’s called triglyceride. The way they attach is just like how the sugars did: it’s another example of a dehydration synthesis reaction (or hydrolysis if the reverse).
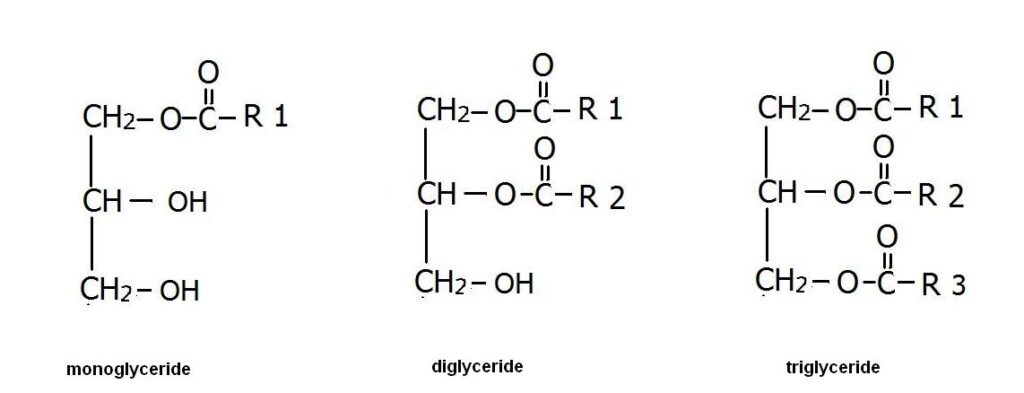
Fat cells, more properly called adipocytes, have a large vacuole where fatty acids from the food we eat are joined with glycerol and are stored as triglycerides. The process is reversible in case we need to use the fat too. If you go to have blood work done, they will check not only your cholesterol but your fat content, known as your lipid panel.
Phospholipids are schizophrenic molecules.
Phospholipids begin with a glycerol molecule and as in the case of a triglyceride, we have fatty acids attached but in place of the 3rd FA is a Phosphate group (PO4).
A phosphate group is polar, which means it tends to have a charge and polar constituents dissolve in water. The PO4 head of the molecule is hydrophilic (it likes water!). Fats are hydrophobic. So what we have in this case is a schizophrenic molecule. One part of it likes water and the rest of it hates water. As shown below the top part represents the phosphate (hydrophilic) part and the two strings are the fatty acids which are hydrophobic.
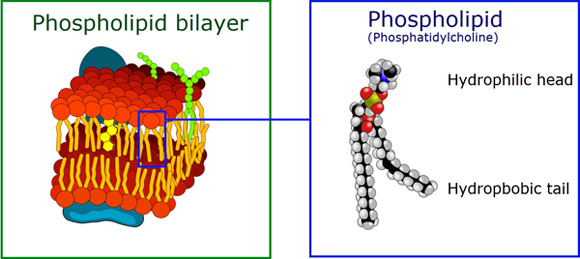
To learn more about the function of the phospholipid bilayer and the organelles, review the building blocks of cells.
Steroid Hormones (androgens, female sex hormones, mineralcorticoids, glucocorticoids)
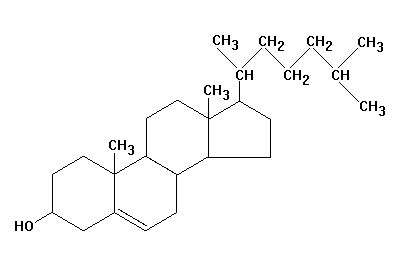
The last category of fats are steroids. Everybody has heard of steroids but nobody really understands what they are. Cholesterol, which is synthesized in the liver, is the starting material for synthesis of other steroids in the body. What does cholesterol actually look like? Let the picture on the right sink in a bit.
We get cholesterol in two ways: (1) Anything from animals contain cholesterol. Egg yolks are considered the highest containing cholesterol’s. (2) Our livers are able to convert saturated fats into cholesterol. In other words if we have a long chain of carbon atoms (saturated fats), they can be folded and joined together into rings to become cholesterol. So if you want to reduce the amount of cholesterol you have in your body, you have to reduce saturated fats as well.
The way that lipitor and the other statin drugs work (the reason it’s called statins is because the generic names of all these drugs end with -statin) is they inhibit the enzyme that turns saturated fat into cholesterol.
The reason for this is because it’s impossible to cut out all saturated fat. Remember from the chart above, even coconut oil is 92% saturated fat.
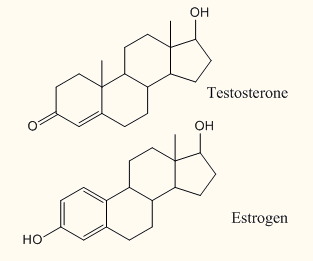
Look on the right: Although the chemical structures of testosterone and estrogen are very similar, their subtle differences make a HUGE difference in the way they work.
The only people who need to lower their cholesterol levels are ones who have high levels to begin with, otherwise it is totally healthy. You could relate that to sugar, which is the most common food. We all need sugar but if we eat too much of it, that leads to diabetes. We all need salt, we would die without it, but too much of it will lead to high blood pressure. So we need these things, it’s just that they are bad with too much of it.
(A) Androgens are steroids.
Androse means male. An android means a male-looking robot. These are masculanizing hormones. The first one is testosterone. The second is adrenalandrogen. Androgenic hormones like testosterone have a number of effects on the cells of our body as they affect biochemical reactions. That’s what drugs do, they affect chemicals in the body.
1) Testosterone actually increases anabolic reactions. Anabolic biologic reactions are growth reactions. You’ve heard of anabolic steroids, right? Androgens promote growth and promote muscles. Males are taller and more muscular because of testosterone. Testosterone also increases catabolic reactions which is for energy production. As a result, males metabolize food faster than a female. This is also why a male runs faster and jumps higher. Another effect is that it increases hair growth. The only place it doesn’t increase it on the top of the head. Another thing it increases is libido.
2) Adrenoandrogen’s are produced from the adrenal glands which are located above the kidney. This is just one of them. This hormone is produced not only in men but women and is a much weaker drug than testosterone and doesn’t affect men that much because they have so much testosterone. The main effect this has on women is that it increases hair growth and libido.
(B) Female Sex Hormones are steroids.
1) Estrogen is created in the ovaries. Estrogen is to females as testosterone is to males. Similar to the way testosterone makes a man grow larger, estrogen promotes the increase of breast size and deposition of fats in the hips.
2) Progesterone is also produced in the ovaries. There is no counterpart to progesterone in men. The hint of what it does is in the word: “pro-” means to prepare and “gest” means pregnancy (gestation). It is secreted every month in the woman and prepares a woman’s month for pregnancy. It increases vascularization (growth of blood vessels) of the endometrium of the uterus. If an egg is fertilized, then this egg will implant in the uterus. If she doesn’t get pregnant or is not even sexually active then those blood vessels are shed. That shedding of blood vessels is called “having a period” or menstruation. When that happens, she knows she didn’t get pregnant that last month. Funny fact: A 19th century physiology book says that a period occurs because a woman is crying because she’s not pregnant.
(C) Mineralcorticosteroids are steroids.
Mineralcorticosteroids are created in the cortex of the adrenal gland. Remember the outer part is the cortex while the inner part is the medulla (just like how there’s a cerebral cortex in the brain, and the inner part is the medulla oblongata, same way in the kidneys, renal cortex and renal medulla). These control the mineral balance (Na+ & K+) in the body.
(D) Glucocorticosteroids are steroids.
Gluco means glucose. Cortico means cortex. These raise the blood glucose level most especially during stress.
(E) Cholecalciferol aka Calciferol aka Vitamin D, is a steroid.
Cholecalciferol is also known as Vitamin D that is made in your skin. Chole means cholesterol and is created when UVB sun rays hit cholesterol to change the molecule into cholecalciferol. Vitamin D helps aid in the absorption of calcium in the small intestine (which is why the word calci is in the name).
Relevant article: The Offbeat Reason Why Cats and Dogs Lay In The Sun and Lick Their Fur
Let’s pretend you pour yourself a glass of milk. Milk is especially high in calcium. However you won’t be able to absorb this hormone if you don’t have this Vitamin D hormone. There’s not a lot of farmers or carpenters these days; Most people work indoors, including kids who used to play baseball are now playing video games inside. People are increasingly spending less time in the sun. We are not getting enough of this hormone so that people will be able to absorb the milk. This is why they add Vitamin D3 is added in milk. If you read on every milk carton it says Vitamin D is added. If they called this a steroid hormone, nobody would give this milk to their kids, so it’s called “Vitamin D.” New studies show that we need this not only for calcium absorption but also DNA synthesis and to reduce cancer rates.
So to recap this article as a simple outline we have…
1) Fatty Acids: Saturated, Monounsaturated, Polyunsaturated fats.
2) Prostaglandins create inflammation. NSAID’s help reduce it.
3) Monoglyceride, Diglyceride, Triglycerides all contain 3 carbons (glycerol) with 1, 2 or 3 attached FA’s, respectively.
4) Phospholipids are like triglycerides with a polar, hydrophilic phosphate head in place of the third FA.
5) Steroid hormones all start as cholesterol as the source which is basically long chains of saturated fats joined to become rings. Note that many steroids hormones end with “-one.”
Androgens: Testosterone and Adrenoandrogen
Female sex hormones: Estrogen and Progesterone
Mineralcorticoids, Glucocorticoids and Cholecalciferol.
Now let’s learn about the next organic compound.. Proteins!






