Growth Hormone (Somatotropin)
The hypothalamus releases the following Releasing Hormones that stimulate the release of different hormones from the adenohypophysis:
- Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (C.R.H. causes the release of ACTH)
- Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (T.R.H. causes the release of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone aka Thyrotropin)
- Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH releases LH and FSH.)
- Growth Hormone R.H. & Growth Hormone I.H.
- Prolactin R.H. & Prolactin I.H.
In this post, we’re concerned with #4.
Growth Hormone is a non-tropic hormone: Its function is to stimulate growth in the body, especially the skeletal system and the muscles. G.H. increases protein synthesis and most of the protein in our body is in our muscle cells in the form of actin and myosin. A lot of athletes take G.H. injections (that’s what Barry Donds of the Giants was doing).
Interestingly, while increased protein synthesis is anabolic, it also promotes the break down of glycogen in the liver (glycogenolysis) and lipolysis. It’s kind of like, anti-cortisol because cortisol promotes the breakdown of protein for energy which changes to sugars then fats. G.H. synthesizes protein and breaks down sugars and fats for energy.
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GhRH) causes the release of growth hormone and Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH aka Somatostatin) inhibits it. Just like prolactin and the mammary gland, there’s no way the GH can go back to the pituitary to create a negative feedback loop. A deficiency of G.H. during childhood means the childs bones wont grow normally, which is dwarfism. Don’t confuse this with cretinism, associated with hypothyroidism which affects development of the brain as well.
 An excess of growth hormone in children results in gigantism where the bones grow too much and they could be 7 to 9 feet tall. An excess of GH in an adult will cause the bones to grow thicker and that’s called acromegaly. Your bones only grow so long, and by the time you’re in your low 20’s, you’ve reached your maximum height no matter if you take G.H. or not. But it will cause the bones to grow thicker and that’s called acromegaly. (Barry bonds didn’t grow taller, only wider).
An excess of growth hormone in children results in gigantism where the bones grow too much and they could be 7 to 9 feet tall. An excess of GH in an adult will cause the bones to grow thicker and that’s called acromegaly. Your bones only grow so long, and by the time you’re in your low 20’s, you’ve reached your maximum height no matter if you take G.H. or not. But it will cause the bones to grow thicker and that’s called acromegaly. (Barry bonds didn’t grow taller, only wider).
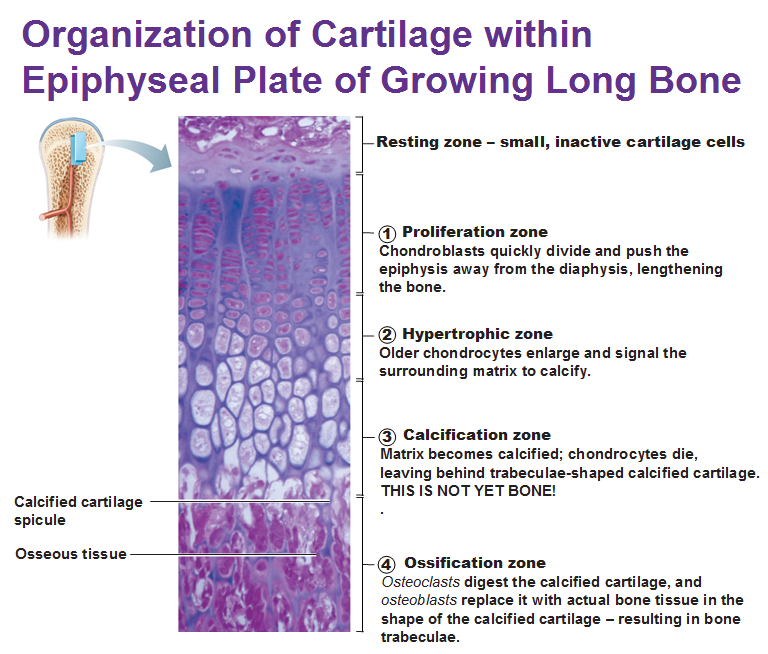
Last thing, something you learned in anatomy: Growth hormone stimulates the growth of bones and how does it actually make our bones grow longer/taller? By stimulating the growth of myelin cartilage (endochondral bone formation). The end of a growing, long-bone is called the epiphysis.
The shaft is the diaphysis. The area between the epiphysis and diaphysis is called the epiphyseal plate. That’s the last place on the bone that has hyaline cartilage.
See it says resting zone and proliferation zone and calcification zone? Growth Hormone stimulates the growth of cartilage at the zone of resting cartilage. When all the hyaline cartilage has turned to bone tissue, your bone can no longer grow longer. When you see the x-ray of a child you see the epiphyseal plates but in an adult you don’t because it looks like solid bone. So while the bones cannot grow longitudinally, they can grow appositionally in length.







